Tempered Glass Vs. Heat-Strengthened Glass
As the name suggests, safety glass is specially designed to be less prone to breakage and reduce the possibility of causing injury to people. It also refers to glass that is intended to be made for added strength and fire resistance. In general, it comes in two types: tempered glass and heat-strengthened glass.
The Tempered Glass
Also called toughened glass, tempered glass is made by heating the regular annealed glass evenly which is then cooled rapidly through the uniform blowing of air onto both sides of the glass at the same time, this a process called air quenching. This rapid cooling process is done to increase both the compression force and tension force on the surface and inside of the glass. This makes tempered glass four times stronger than its regular annealed glass counterpart of the same size and thickness. Tempered glass comes in various forms of thicknesses, ranging from 1/8" to 3/4". Tempering is known to increase the tensile strength of safety glass, making it more able to resist damaging forces due to harsh weather elements and impact. It is used in appliances such as ovens and stoves that are often exposed to high-temperature heat and it is also used in car windshields to prevent large shards of glass in case of an accident.
The Heat-Strengthened Glass
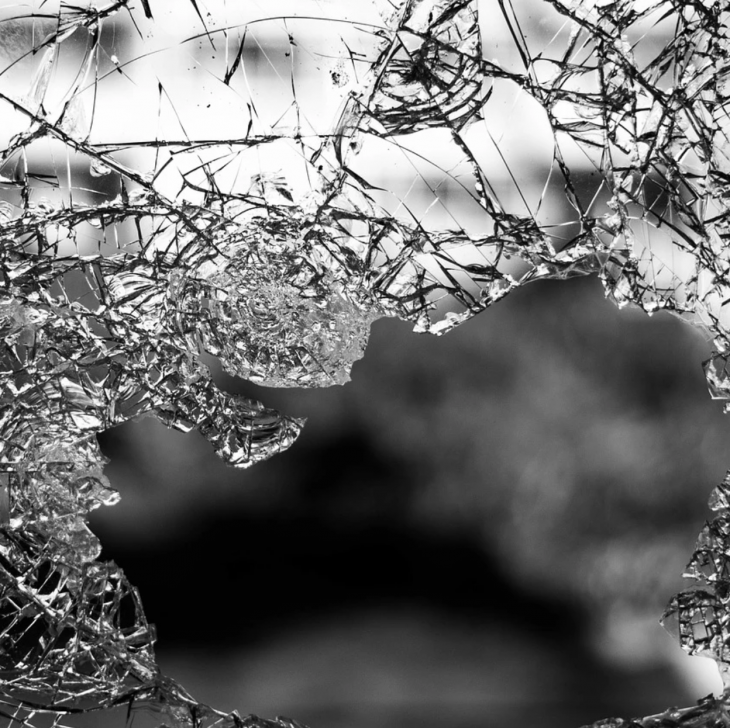
This type of glass is created by putting an annealed glass under high heat and then cooling it at a slower rate which directly affects the strength of the glass. As such, stronger glass can be made by changing or modifying the rate of cooling. Once heat-strengthened glass breaks, it shatters into large, jagged pieces of glass, making it less qualified to being considered as safety glass. Since it has great thermal stress, it is usually used in high-rise buildings. Also, it is about twice as strong as regular annealed glass of the same size and thickness, making it more resistant to impacts.

As the name suggests, safety glass is specially designed to be less prone to breakage and reduce the possibility of causing injury to people. It also refers to glass that is intended to be made for added strength and fire resistance. In general, it comes in two types: tempered glass and heat-strengthened glass.
The Tempered Glass
Also called toughened glass, tempered glass is made by heating the regular annealed glass evenly which is then cooled rapidly through the uniform blowing of air onto both sides of the glass at the same time, this a process called air quenching. This rapid cooling process is done to increase both the compression force and tension force on the surface and inside of the glass. This makes tempered glass four times stronger than its regular annealed glass counterpart of the same size and thickness. Tempered glass comes in various forms of thicknesses, ranging from 1/8" to 3/4". Tempering is known to increase the tensile strength of safety glass, making it more able to resist damaging forces due to harsh weather elements and impact. It is used in appliances such as ovens and stoves that are often exposed to high-temperature heat and it is also used in car windshields to prevent large shards of glass in case of an accident.
The Heat-Strengthened Glass
This type of glass is created by putting an annealed glass under high heat and then cooling it at a slower rate which directly affects the strength of the glass. As such, stronger glass can be made by changing or modifying the rate of cooling. Once heat-strengthened glass breaks, it shatters into large, jagged pieces of glass, making it less qualified to being considered as safety glass. Since it has great thermal stress, it is usually used in high-rise buildings. Also, it is about twice as strong as regular annealed glass of the same size and thickness, making it more resistant to impacts.